There are lots of different names for space rocks, but what do they all mean?
In this handy FAQ, get to know asteroids, meteorites and other celestial bodies that Earth encounters as it travels around the Sun.
What’s the difference between asteroids and comets?
Asteroids and comets both orbit the Sun and formed around the time that our solar system was born. The main difference between them is what they’re made of.
Asteroids are rocky or metallic objects that can be a few meters to hundreds of metres in diameter. Some are material that’s loosely scooped together, while others may be more solid with metallic cores.
Most asteroids are found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.

Rocks collected from the surface of the asteroid Bennu indicate that asteroids may have delivered some of the ingredients for life to Earth. Image © NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio via Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain
Comets are composed of dust, rocky material and ice – they’re like big, dirty snowballs.
Comets come from the Kuiper Belt beyond the planet Neptune and the Oort Cloud at the edge of the solar system. As comets get close to the Sun, the warmth makes them release gases, which can form a visible tail behind them.
What are meteors, meteorites and meteoroids?
Sometimes large bodies in space, such as asteroids, bump into each other. If they collide with enough force, bits can get knocked off and begin to travel through space. These smaller fragments are called meteoroids.
If a meteoroid enters Earth’s atmosphere, its name changes. We call these objects meteors. Most meteors you see in the form of shooting stars – meteor showers – are dust-sized particles that burn up as they pass through the atmosphere, creating streaks of light in the sky.
Sometimes large meteors don’t completely burn up. If they survive their journey through the atmosphere and land on the ground, these extraterrestrial objects are known as meteorites.

Meteorites are usually named after where they’re found. This is the Winchcombe meteorite, which fell in February 2021. It’s a type of meteorite known as a carbonaceous chondrite.
What is a meteor shower?
Meteor showers occur when Earth passes through debris left behind by comets and asteroids as they pass close to the Sun. The result can be spectacular displays of as many as hundreds of meteors flashing across the sky like natural fireworks.
Get tips on how to watch the next meteor shower.
Where do meteorites come from?
Most meteorites are fragments that have broken away when two asteroids collide. Meteorites can also come from comets and a rare few come from the Moon and Mars.
Scientists can tell if meteorites are from the Moon as their composition is very similar to samples brought back from the Apollo lunar missions.
While Martian meteorites may look like rocks from Earth, they can be identified due to their similarities to Mars’s atmospheric composition, which was detected in the 1970s by the Viking probe.
How old are meteorites?
Meteorites from asteroids are around 4.5 billion years old.
Meteorites from the Moon are older than 2.5 billion years, and meteorites from Mars may be as young as 165 million years.
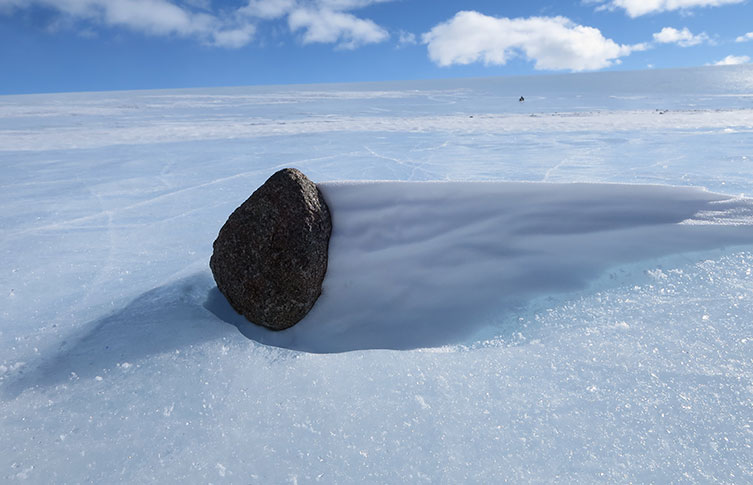

A meteorite found in Antarctica. Image © Nancy Lanza via NASA Johnson Flickr, licensed under CC BY-NC 2.0
Where do scientists find meteorites?
Although few meteorites are observed hitting the ground – most fall into the sea – thousands of meteorites are collected each year.
Meteorites can be found all over the world – including in the UK – but are easiest to spot in dry places, such as the desert in Australia or Antarctica. In these places they erode more slowly and are less likely to be hidden by vegetation.
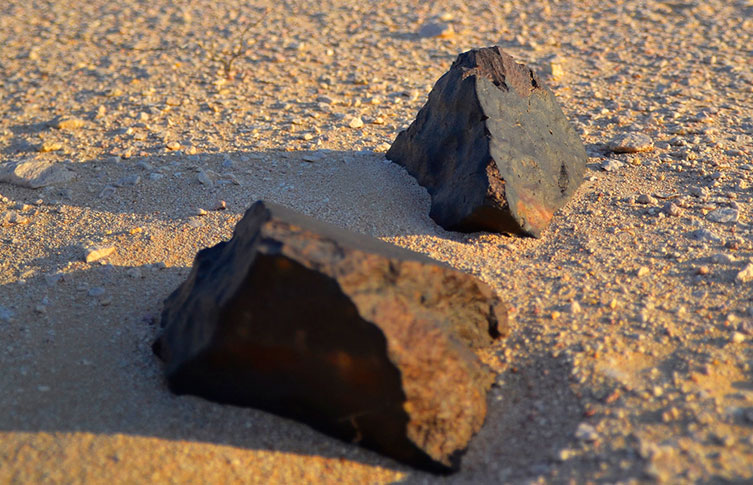

A meteorite found in the desert. Image © Marek Woźniak via Wikimedia Commons, licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0
Are meteorites radioactive?
No. Meteorites do contain radioactive elements, but not significantly more than any ordinary terrestrial rock.
Have scientists found alien bacteria in meteorites?
No evidence of extraterrestrial organisms has been found in meteorites.
In fact, we haven’t found any signs of extraterrestrial life in space yet – but some think we may find evidence of it in our own solar system.
Did a meteorite or asteroid kill the dinosaurs?
Evidence suggests that an asteroid collided with Earth 66 million years ago in the Cretaceous Period. It’s believed to have contributed to a mass extinction of around 75% of all species living at the time, including many dinosaurs.
This asteroid would have caused immediate devastation in the vicinity. Secondary effects, such as ash and dust blocking out the Sun, would have caused a global collapse of the food chain. Discover more about the extinction of the dinosaurs.
Has anyone been killed by a meteorite?
There have been no recorded deaths due to a meteorite fall. The chances of witnessing a meteorite fall, let alone being hit by one, are very, very small.
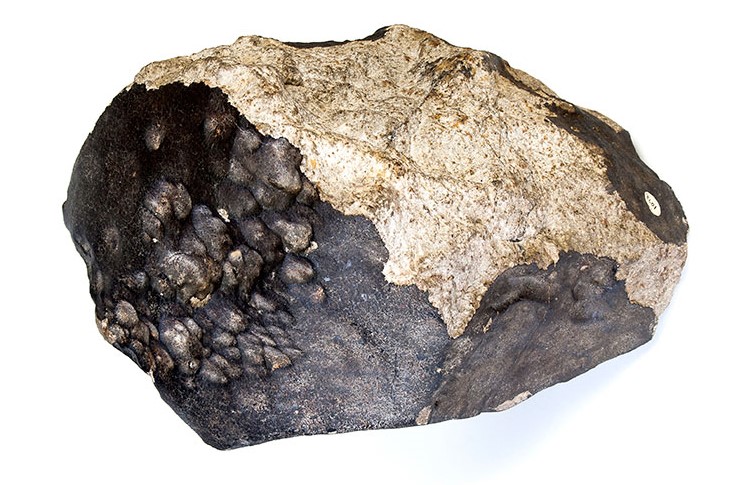

When the Wold Cottage meteorite fell in December 1795, it caused an impact crater about 50 centimetres deep. A farmworker was so close to the impact site that he was struck by the soil and rocks thrown into the air by the meteorite’s crash landing
What was the largest meteorite to ever hit Earth?
Vredefort Dome in South Africa is the largest impact crater on Earth. It’s very ancient – around two billion years old – and poorly preserved, but measures roughly 300 kilometres across. The asteroid would have been enormous, possibly up to 25 kilometres in diameter.
How often do major meteorite impact events occur?
Scientists predict that a meteorite around 30 to 50 metres across, capable of forming a kilometre-wide crater, will occur around every 1,000 years. However, the last impact of this size that we know of took place 55,000 years ago.
Would we have warning of a large meteorite impact? Are we prepared?
Asteroid and comet collisions with Earth are a natural hazard.
However, while it’s likely that Earth will be hit by something eventually, global observation networks are keeping constant vigil, so there should be plenty of warning about potential impacts. Experts are constantly improving their ability to detect and deflect asteroids.

Explore space
Discover more about the natural world beyond Earth's stratosphere.

Space: Could Life Exist Beyond Earth?
Snap a selfie with a piece of Mars, touch a fragment of the Moon and lay your hands on a meteorite older than our planet before our exhibition’s mission ends.
Closes Sunday 22 February 2026



Don't miss a thing
Receive email updates about our news, science, exhibitions, events, products, services and fundraising activities. We may occasionally include third-party content from our corporate partners and other museums. We will not share your personal details with these third parties. You must be over the age of 13. Privacy notice.
Follow us on social media