Conodonts are extinct phosphatic microfossils that 'look like' teeth and are used extensively for dating rocks roughly 500-205 million years old. Ever since they were first described as fish teeth by C. H. Pander in 1856 they have caused arguments over how they should be classified and, nearly 150 years later, continue to do so. Read on to find out if they really are teeth, why they are so difficult to classify, give names to and even decide which way up they should be!
Images of platform, blade-like and coniform conodonts from the Museum collection. Note the presence of white matter inside and beneath the denticles of some of the specimens, a feature unique to conodonts.
For consistency, I shall refer to these individual phosphatic elements as conodonts and the creature that produced them as the conodont animal. Some consider this incorrect; you wouldn't refer to the 'cat animal' or the 'lion animal' for example. Often the individual specimens are referred to as conodont 'elements'.
- What do they look like?
Conodonts are generally between 0.1mm to 2mm long, although some examples from a single deposit in South Africa measure up to 20mm. They take a variety of different forms including complex platforms, blade-like structures, simple cones and elongate bars with denticles (i.e. small teeth or tooth-like structures). Each specimen has a basal cavity and depending on preservation and species, white matter can be seen inside.
- How do you find them?
Usually they are found in marine rocks (limestones or shales) and are released by dissolving them in acetic acid (the acid constituent of vinegar); a process that can take many weeks and sometimes months. The resulting residues are sieved and concentrated into a heavy fraction containing the conodonts by using a heavy liquid such as sodium polytungstate. The majority of collections consist of disarticulated remains and this is the main issue facing scientists studying their distribution.
A scanning electron microscope image of conodonts from the Silurian of Gotland, Sweden (photograph Dr Paul Taylor, NHM). Although many different shapes can be seen here, the specimens illustrated probably belong to only two species.
- What is a species?
Early conodont workers described each shape encountered under a different species name as nothing was known about the animal that produced them, or even if it was an animal. Despite the later discovery of bedding plane assemblages of individual conodonts arranged in biological position, many workers continued to give separate names to each form.
In the latter stages of the 20th Century, arguments raged over whether to use multielement taxonomy, where different shaped but biologically related elements were grouped together under one species name. Some scientists preferred to continue to name each element separately and as a result, older published literature can be confusing.
A bedding plane assemblage of Idiognathodus from the Carboniferous of Bailey Falls, Illinois, USA. Fused clusters of conodonts and bedding plane assemblages like these are preserved in the fossil record only in exceptional circumstances. They give direct evidence of the biological grouping and positioning of the various elements in the conodont animal. Left: an SEM image. Right: the same specimen photographed under a light microscope. The black scale bar in the middle is about 0.5mm.
- Are they teeth?
Although conodonts look like teeth, it has also been suggested that they could have functioned as sieve structures to filter fine particles. One of my favourite early interpretations of the conodont animal was published by Maurits Lindstrom in 1974. You can imagine these elongate conodonts with upper denticulated surfaces acting very much like a filter if arranged like this.
An interpretation of the conodont animal as published by Lindstrom in 1974. I like to call this the 'loo roll' reconstruction!
Polygonal patterns on the upper surfaces of some conodonts show the impressions of cells and suggest that - at least at some stage - parts of some conodonts were fully enclosed in soft tissue. Wear patterns on the surfaces of conodonts and growth studies based on bedding plane assemblages suggest that for some conodonts, the elongate denticulated conodonts were used in a rasping action to capture food and pass it backwards to more blade and platform shaped cutting and grinding teeth. However, this is not universally accepted with some scientists suggesting that conodonts could not have functioned in a cutting action.
Polygonal microsculpture representing the impressions of cells on the platform surface of the Devonian conodont Ancyrodella.
- What produced them?
The conodont animal was discovered by chance in a Scottish museum in the early 1980s by some scientists looking for shrimp fossils in the Carboniferous Granton Shrimp Bed. This story is often quoted by curators trying to justify the upkeep of large collections as it is an excellent example of a major discovery resulting from an old uncatalogued collection. The discovery ended one of the longest running sagas in palaeontology; what produced the conodonts?
 This is one of 10 specimens from the Granton Shrimp Bed of Edinburgh where details of the body of the conodont animal are preserved. The Museum purchased this specimen in the 1980s at around the time that the first paper on the conodont animal was published. The scale bar shows millimetres so the preserved part of the body is just over 1.5cm long.
This is one of 10 specimens from the Granton Shrimp Bed of Edinburgh where details of the body of the conodont animal are preserved. The Museum purchased this specimen in the 1980s at around the time that the first paper on the conodont animal was published. The scale bar shows millimetres so the preserved part of the body is just over 1.5cm long.
Details from the 10 specimens available were amalgamated to produce a reconstruction of the conodont animal showing that it had an elongate body with chevron shaped muscle blocks, a caudal fin, a notochord running along its body and paired eyes. There are now other examples of soft body preservation of conodont animals including the giant conodont Promissum pulchrum from the Ordovician of South Africa. This has a very similar body plan to the Granton animals.
- How should they be classified?
Although many early conodont workers were only interested in studying the stratigraphical distribution of conodonts for biostratigraphy (relative dating of rocks on the basis of their biological content), between 1876 and 1975 there were 46 different conodont affinities published. Some concluded that they were related to worms, snails, arthropods, chordates and even plants. Others considered them so different from anything else that they should represent a separate phylum, the Conodonta.
The precise interpretation of the preserved soft tissues of the conodont animal and histological sections through conodont hard tissues continues to divide the scientific community. Interpretations of conodont hard tissues as representing enamel, cellular bone and globular calcified cartilage have led many to classify them as early vertebrates placing them as more derived than the living lampreys and hagfish and precursors to the early fishes.
Not all scientists accept this because some vertebrate workers consider the tissues, particularly the conodont white matter, to be unique to conodonts and unrelated to the dentine and bone present in early fishes. This, allied to differing interpretations of the conodont soft tissues has led to suggestions that they are Chordates but unrelated to the Vertebrates.
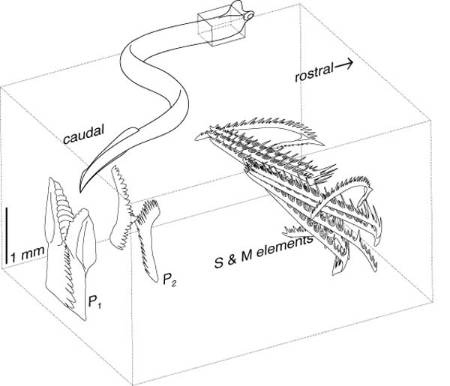
The conodont feeding apparatus and its position within the conodont animal (boxed area) based on Idiognathodus and Clydagnathus respectively. Image courtesy and copyright of Prof. Mark Purnell, University of Leicester. See the text for an explanation of the labels.
- What way up should conodonts be?
Before the discovery of the conodont animal and detailed studies of bedding plane assemblages, the exact biological positioning of conodonts within the mouth part of the conodont animal was conjectural. Various conventions used to describe anterior/posterior, upper/lower and inner/outer have subsequently proven to be incorrect. For example, in old terminology the 'anterior blade' of the P1 element is shown above to be a ventral blade.
P (Primo) elements were considered to be at the front of the mouth and S (Secundo) elements further back. Discovery of the conodont animal has shown that the reverse is true. Element terminology using the terms P, S and M is ingrained in the literature and will never be changed. However, many continue to use outdated terminology to describe anterior/posterior, upper/lower and inner/outer or use similarity of shape to infer similarity of biological positioning within the conodont animal.
- Summary
I have given a very simplistic guide to conodonts here, showing some of the reasons why there have been and still are so many arguments over naming them, working out their function, classifying them and even orientating them. This post is not intended to champion the research of any particular academic or to give strong views on any of the arguments mentioned but if you are interested to receive further details of scientific literature discussing these issues then why not comment below or contact me directly.