Glossary
Glossary terms beginning with: P
show all images
- parafasciole
-
A fasciole in which normal spines and tubercles are interspersed within the band of clavulae. Parafascioles usually have diffuse boundaries.
(show image)
- pedicellaria (-ae)
-
A stalked appendage that ends in a valved head (usually with three valves but occasionally with two, four or five). These valves are connected at their base and are able to open and close. They are used for defence, to deter skin parasites, and to clean the test surface.
(show image)
- pedicellariae
-
pleural of pedicellaria
- penicillate (tube-foot)
-
A tube-foot with a large disc covered in finger-like projections each supported by a calcitic rod and ending in a mucuous pad. Used in detritus feeding and restricted to spatangoids and holasteroids.
(show image)
- perforate (tubercle)
-
A tubercle whose mamelon has a central pore. This pore houses ligament which binds the overlying spine to the tubercle.
(show image)
- perianal
-
Around the apex. Usually referring to tubercles and spines on genital plates that immediately surround the periproct.
(show image)
- perignathic girdle
-
Internal projections originating from the most adoral coronal plates surrounding the peristome and to which lantern protractor and retractor muscles afix.
(show image)
- peripetalous (fasciole)
-
An aboral fasciole band that encircles the petals.
(show image)
- periproct
-
The opening through the test associated with the anus.
(show image)
- periproctal membrane
-
A flexible, usually plated, membrane that covers the periproct and through which the anus opens.
(show image)
- peristome
-
The opening through the test associated with the mouth.
(show image)
- peristomial membrane
-
A flexible, usually plated, membrane that covers the peristome and through which the mouth opens.
(show image)
- perradial
-
At or towards the centre of the ambulacral zone (direction)
(show image)
- perradius
-
Suture separating the two columns of ambulacral plates
(show image)
- petal
-
A zone of enlarged pore-pairs bearing specialized respiratory tube-feet forming the adapical part of an ambulacrum.
(show image)
- phyllode
-
An expanded zone of specialized pore-pairs (and tube-feet) close to the peristome.
(show image)
- phyllopodia
-
An obsolete name for penicillate tube feet.
(show image)
- phymosomatid plate compounding
-
A style of ambulacral plate compounding composed of four or more elements, of which the second lowest element is the largest. The upper and lower elements both extend the full width from adradial to perradial suture, but other elements are short and do not reach the perradius.
(show image)
- plastron
-
The interambulacral plates immediately to the posterior of the mouth in atelostomes, comprising the labral plate (L), sternal plates and sometimes episternal plates (Atelostomata).
(show image)
- platform
-
In a tubercle, the flat or raised zone immediately surrounding the mamelon at the top of the boss. The platform may be crenulate or smooth (as in this picture)
(show image)
- plumula
-
The growing tip of the tooth
(show image)
- polygeminate (plating)
-
A compound plate composed of four or more elements.
(show image)
- pore-pairs
-
The double pores (one inhalent, the other exhalent) that connect the external tube-foot to the internal water vascular system.
(show image)
- pores (ambulacral)
-
A single or double perforation through ambulacral plates which connects the external tube-foot to the internal water vascular system.
(show image)
- pressure channels
-
Slightly depressed zones on the test leading into the lunules or notches (Clypeasteroids).
(show image)
- primary spine
-
The spine associated with the largest tubercle on each ambulacral or interambulacral plate.
(show image)
- primary tubercle
-
A distinctly larger primary tubercle that forms at the growth centre of the plate. There is one primary tubercle to each plate.
(show image)
- primordial plate
-
The first formed interambulacral plate which is unpaired and forms the edge to the peristome. It is resorbed in many regular forms during development but is retained in most irregulars. Also referred to as the basicoronal plate.
(show image)
- protosternous (plastron)
-
Plating of posterior interambulcarum on oral surface in atelostomates where the first (basicoronal) plate (red) is small and undifferentiated.
(show image)
- protractor muscles
-
Muscles connecting the pyramids to the perignathic girdle and used to project the lantern out the test.
(show image)
- pseudobourrelet
-
A raised zone of interambulacral plates approaching the peristome and supporting a grill of spines over the opening. Unlike bourellets these are constructed from a number of small adoral interambulacral plates.
(show image)
- Pseudocompound plating
-
A style of ambulacral plate compounding composed of three elements, of which only one is enlarged and supports the primary tubercle - the other two are reduced to small platelets lacking tubercles. This is the typical plating of echinothurioids.
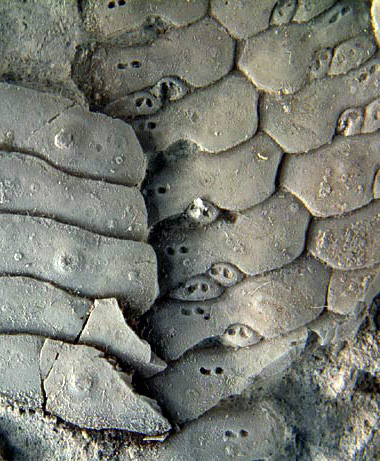
- pyrinid plating
-
A style of ambulacral plate compounding composed of three elements, of which the middle is reduced to a tiny adradial element.
(show image)
|